Breaking Down the Components: A Deep Dive into SMD Screen Technology
In today’s fast-paced digital world, the demand for visually captivating displays has never been greater. From the screens of our smartphones to the billboards that line the city streets, we are surrounded by an array of stunning visuals that captivate our attention and deliver information with utmost clarity. At the heart of this visual revolution lies Surface Mount Device (SMD) screen technology, a powerful and innovative solution that has become the backbone of modern display systems.
In this article, we will take a comprehensive deep dive into the intricacies of SMD screen technology, unraveling its components, functionality, and the unparalleled advantages it brings to the forefront. Prepare to embark on an enlightening journey as we explore the inner workings of SMD screen technology and discover the key behind its triumph in the world of displays.
Table of Contents
- Screen Technology and Its Evolution in the Digital Age
- Understanding Surface-Mounted Device (SMD) Screens: An In-Depth Analysis
- Key Components of SMD Screen Technology: Exploring the Building Blocks
- Optimizing Performance and Enhancing User Experience: Best Practices for SMD Screen Implementation
- Q&A
- Closing Remarks

Screen Technology and Its Evolution in the Digital Age
Screen technology has come a long way in the digital age, with SMD (Surface Mounted Device) screens leading the charge in terms of innovation and quality. These screens consist of several components that work together to create stunning visuals and an immersive user experience.
At the heart of SMD screen technology are LED (Light Emitting Diode) displays, which provide bright and vibrant colors. LED technology allows for better contrast, improved readability, and reduced energy consumption compared to older screen technologies. The LEDs are arranged in a grid pattern and emit light when an electrical current is applied. This grid pattern is what gives SMD screens their seamless and smooth appearance, as multiple LED panels are seamlessly connected to form a larger screen.
Another important component of SMD screens is the driver IC (Integrated Circuit). This IC is responsible for controlling the brightness and color levels of individual LEDs. By precisely controlling the output of each LED, the driver IC ensures that the SMD screen delivers accurate and consistent colors across the entire display. Additionally, the driver IC also helps to reduce power consumption and extend the lifespan of the LED panels.
To protect the delicate LED panels and driver IC, SMD screens are enclosed in a rugged and durable housing. This housing is typically made from high-quality materials that can withstand harsh weather conditions and resist damage from external impacts. The design of the housing also plays a crucial role in the overall performance of the SMD screen, as it helps to dissipate heat and prevent overheating.
In conclusion, SMD screen technology represents a significant evolution in the digital age. By combining LED displays, driver ICs, and robust housings, these screens offer unparalleled image quality, energy efficiency, and durability. Whether used for outdoor advertising, indoor displays, or large-scale event screens, SMD screens continue to revolutionize the way we view and interact with digital content.
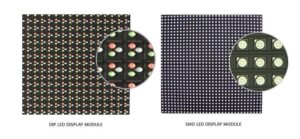
Understanding Surface-Mounted Device (SMD) Screens: An In-Depth Analysis
Surface-Mounted Device (SMD) screens are a vital component in the world of modern technology. These screens are intricate, compact, and highly efficient, making them the preferred choice for a wide range of electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and televisions. In this comprehensive analysis, we will delve deep into the components that make up SMD screen technology, unraveling the secrets behind their exceptional performance and functionality.
One of the key elements of an SMD screen is its display module. This module comprises a thin-film transistor (TFT) layer, which acts as a pixel switch, controlling the flow of electrical current to each individual pixel on the screen. The TFT layer is supported by a color filter layer, responsible for adding vibrant and accurate colors to the display. Additionally, a backlight unit (BLU) provides the necessary illumination for the pixels to produce visible images. The combination of these components results in a high-resolution, visually striking display that captivates the viewer’s attention.
In addition to the display module, SMD screens also feature numerous other crucial components, each playing a vital role in their overall performance. These include a timing controller (T-CON), responsible for synchronizing the image data and transmitting it to the display module; a data driver, which converts the digital image data into analog signals that can be interpreted by the display module; and a power supply unit (PSU), ensuring a stable and reliable power source for the screen’s operation. All these components work harmoniously together, creating a seamless user experience that is both visually stunning and technologically advanced.
To summarize, the world of SMD screen technology is a fascinating one, with its complex yet highly refined components working together to deliver exceptional displays. Understanding the various elements that make up an SMD screen provides valuable insight into the intricacies of modern electronic devices. From the display module to the timing controller and power supply unit, each component plays a crucial role in creating the vibrant, high-resolution displays that we have come to expect from our everyday devices.
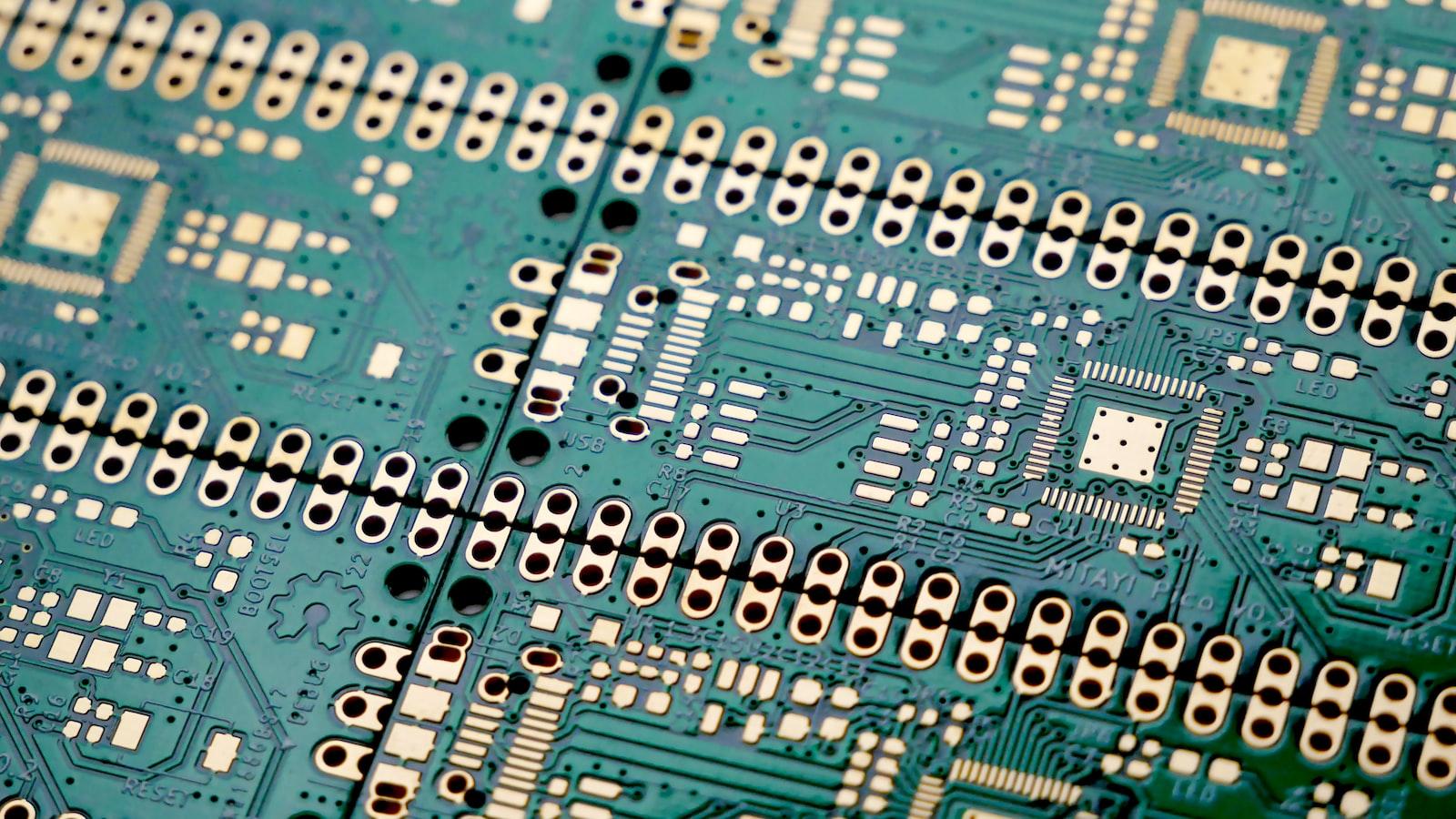
Key Components of SMD Screen Technology: Exploring the Building Blocks
Screen technology has come a long way in recent years, and one of the most innovative advancements is the Surface Mount Device (SMD) screen technology. This groundbreaking technology has revolutionized the way we experience visuals, providing stunning clarity and brightness. In this article, we will delve into the key components that make up SMD screen technology and explore how each one contributes to its remarkable performance.
- LED Pixels: At the heart of any SMD screen is its pixels. SMD screens utilize LED (Light Emitting Diode) pixels, which are tiny semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. These pixels are the building blocks of the screen, and their quantity and arrangement determine the screen’s overall resolution. The pixels are precisely manufactured and placed close together to create a seamless, high-resolution display.
- SMD Modules: SMD screens are composed of small, modular units known as SMD modules. These modules contain groups of pixels that work together to produce a single color. Each SMD module consists of a printed circuit board (PCB) that houses the LEDs, driver chips, and other essential components. The PCB is carefully designed to optimize the electric current flow and ensure the pixels operate at their maximum efficiency. SMD modules are then neatly arranged and connected to form the complete screen, offering flexibility, easy maintenance, and potential for scalability.
In summary, SMD screen technology is a marvel of engineering, seamlessly combining LED pixels and modular SMD modules to create visually stunning displays. Whether it’s for advertising, entertainment, or information purposes, SMD screens offer exceptional brightness and resolution. The key components of LED pixels and SMD modules work together to create breathtaking visuals that captivate audiences and elevate the viewing experience to new heights.

Optimizing Performance and Enhancing User Experience: Best Practices for SMD Screen Implementation
In order to optimize the performance and enhance the user experience of SMD screen implementation, it is important to understand the various components that make up this technology. By delving deeper into the components, we can uncover the best practices for achieving optimal results.
One key component is the LED module. When selecting the LED module for your SMD screen, it is crucial to consider factors such as pixel pitch, brightness, and color uniformity. Pixel pitch refers to the distance between each LED on the module, and choosing the appropriate pitch is essential for achieving the desired resolution. Additionally, brightness plays a significant role in ensuring that the screen is easily visible in various lighting conditions. Finally, color uniformity ensures that the colors displayed on the screen appear consistent and accurate.
Another important component to consider is the driver IC, which controls the brightness and color of the LEDs. It is crucial to select a driver IC that is compatible with the LED module and offers advanced features such as calibration and grayscale control. This allows for precise control over the brightness and color levels, resulting in a more vibrant and accurate display. Additionally, using a driver IC with a higher refresh rate can minimize flickering and motion blur, leading to a smoother viewing experience.
By understanding and implementing these best practices, you can ensure that your SMD screen implementation delivers optimal performance and an enhanced user experience.
Q&A SMD Screen Technology
Q: What is SMD screen technology?
A: SMD stands for Surface Mount Device, and SMD screen technology refers to the use of surface mount components in the construction of electronic displays. These screens are widely used in various applications such as televisions, computer monitors, outdoor advertising displays, and mobile devices.
Q: How does SMD screen technology differ from other display technologies?
A: Unlike traditional display technologies, SMD screens are built using surface mount technology, which allows for smaller and more compact designs. This technology enables manufacturers to produce displays with higher pixel densities, wider viewing angles, and improved picture quality. Additionally, SMD screens offer better energy efficiency and durability compared to other display technologies.
Q: What are the primary components of SMD screens?
A: The main components of SMD screens include LED chips, drive ICs (Integrated Circuits), PCB (Printed Circuit Board), connectors, and various supporting materials such as solder paste and epoxy resin. These components work together to create a functioning display unit.
Q: How do LED chips contribute to SMD screen technology?
A: LED chips are the key component of SMD screens. These chips are responsible for emitting light and creating the visual content on the display. The size, quality, and arrangement of the LED chips significantly impact the resolution, color accuracy, and overall performance of the display.
Q: What role do drive ICs play in SMD screens?
A: Drive ICs, also known as driver Integrated Circuits, are responsible for controlling the voltage and current supplied to the LED chips. They convert the incoming data signals into appropriate electrical signals to ensure the correct functioning of the LEDs. These ICs are crucial for maintaining image clarity and stability on the screen.
Q: How is the PCB important in SMD screen technology?
A: The Printed Circuit Board serves as the foundation for the electrical connections between various components in an SMD screen. It allows for the distribution of power, signal processing, and data transmission. The quality and design of the PCB greatly influence the overall performance and reliability of the display.
Q: Why are connectors essential in SMD screens?
A: Connectors are used to establish electrical connections between different parts of the display module. They ensure efficient communication between the PCB and other components, such as the input source or power supply. High-quality connectors play a vital role in achieving reliable signal transmission and reducing potential issues such as signal loss or damage.
Q: What is the significance of supporting materials like solder paste and epoxy resin?
A: Supporting materials such as solder paste and epoxy resin are used during the manufacturing process of SMD screens. Solder paste enables the connection of various components to the PCB through a process called soldering. Epoxy resin, on the other hand, is used to encapsulate the display module, providing protection against physical damage, moisture, and dust.
Q: How does SMD screen technology contribute to better visual experiences?
A: With advancements in SMD screen technology, displays have become more vibrant, sharper, and capable of rendering a wider color gamut. Higher pixel densities enable smoother images and reduced pixelation, while wider viewing angles ensure consistent image quality from different perspectives. Overall, SMD screen technology enhances visual experiences by delivering more realistic and immersive content.
Q: What benefits does SMD screen technology offer over other display technologies?
A: SMD screen technology offers several advantages over other display technologies. These include better energy efficiency, enhanced picture quality, improved durability, and increased design flexibility. SMD screens can be produced in various form factors and sizes, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Additionally, their compact size and lightweight nature allow for easier installation and transportation.
Closing Remarks
In conclusion, understanding the intricate components of SMD screen technology is key to appreciating the visual wonders it brings to our everyday lives. By delving into the details of this innovative technology, we have explored the value and sophistication of surface-mounted device screens, including their superior brightness, contrast ratio, and breathtaking image quality. As we have examined the fundamental elements that make up these screens—the pixels, backlighting, and various other components—we have gained a deeper insight into their intricate workings.
From television screens and laptop displays to smartphones and advertising billboards, SMD screens have permeated our modern world, revolutionizing the way we consume visual content. Their ability to provide captivating visuals in various sizes and resolutions has unlocked endless possibilities in fields such as entertainment, communication, and advertising.
As technology continues to evolve, SMD screen technology will undoubtedly continue to push boundaries and exceed our expectations. Harnessing the power of advanced manufacturing processes and cutting-edge materials, future iterations of SMD screens hold the promise of even greater color accuracy, energy efficiency, and seamless integration into our daily lives.
In this article, we have taken a comprehensive dive into the world of SMD screen technology, shedding light on its countless components and their vital roles. We hope that this exploration has not only increased your knowledge but also fostered a deeper appreciation for the intricate craftsmanship behind the mesmerizing visuals that SMD screens deliver.
As we move forward, let us embrace the ever-evolving advancements in SMD screen technology, marvel at their immersive displays, and relish the profound impact they continue to have on our visual experiences.
Looking for premium SMD screens and professional display solutions? SMDLED.PK is your trusted partner for state-of-the-art SMD technology. Explore our top-quality products like the stunning Leyard HDR 4K SMD Video Wall for crystal-clear visuals, the versatile MSA Plus SMD LED Screen Module, the sleek MSA Ultra Thin SMD LED Screen Module for modern setups, the durable MSG Outdoor SMD LED Screen Module, and the efficient MSG Indoor SMD LED Screen Module perfect for indoor environments.
We also offer exceptional Outdoor SMD Screens, Indoor SMD Screens, Flexible SMD Screens for creative designs, Cabinet SMD Screens for secure setups, Signpole SMD Screens for advertising, and stunning SMD Video Walls for large-scale visual impact. With SMDLED.PK, experience reliability, superior technology, and tailored solutions for all your display needs. Visit us today and transform your spaces with unparalleled visual excellence!
Contact Us For Free Consultation at 0306-1333384
Powered By BIACommunication

